
In the bustling heart of Singapore, Active Mobility Devices (AMDs)—spanning Personal Mobility Devices (PMDs), Power Assisted Bicycles (PABs), and Personal Mobility Aids (PMAs)—have become indispensable to the city’s vision of a connected and accessible urban mobility landscape. These devices, celebrated for their convenience and efficiency, offer a versatile solution to the challenges of urban transportation, catering to a wide array of commuting needs and preferences. Their integration into Singapore’s transportation ecosystem reflects a forward-thinking approach to embracing sustainable and inclusive mobility options.
Recent years have seen a commendable decrease in fire incidents related to PMDs, a testament to the effectiveness of Singapore’s stringent regulatory measures. These regulations, aimed at ensuring the safety and reliability of these devices, have played a pivotal role in safeguarding public safety. However, despite these advances, the risk of fires remains a pertinent concern across the broader spectrum of AMDs. This enduring risk underscores the need for continued vigilance and adherence to safety protocols, not only for PMDs but for all types of Active Mobility Devices. As Singapore continues to champion the use of AMDs, the commitment to minimizing fire risks through regulation, education, and technology remains crucial in sustaining the safe and harmonious integration of these devices into our daily lives
The Evolution of AMDs in Singapore’s Urban Mobility
Given how AMDs are pivotal components of Singapore’s urban mobility scene, it is important to understand how these devices have evolved and their impact on the urban landscape.
Broadening Horizons with AMDs
Singapore’s urban mobility has been revolutionized by the introduction and integration of various AMDs. These devices, each serving distinct needs and preferences, include PMDs such as electric scooters, PABs which combine the efficiency of pedal power with electric propulsion, and PMAs like motorized wheelchairs, catering to individuals with mobility impairments. This diverse range of AMDs has not only enhanced mobility and convenience but also ensured that the benefits of modern transportation are accessible to all segments of the population.
Enhancing Mobility and Convenience
The presence of AMDs in Singapore’s urban fabric has led to a transformative shift in how residents navigate the city’s bustling streets. PMDs offer a quick and easy means of covering short distances, perfect for the last-mile connectivity from public transport stations to homes or workplaces. PABs, on the other hand, provide an efficient and sweat-free alternative for longer commutes, combining the benefits of cycling with electric assistance. PMAs play a crucial role in fostering inclusivity, enabling individuals with mobility challenges to participate more fully in community life and access services with ease.
Promoting a Greener and More Inclusive Urban Environment
Beyond the convenience and mobility enhancements, AMDs carry significant environmental and social benefits. By reducing reliance on fossil fuel-powered vehicles, these devices contribute to lowering urban air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions, aligning with Singapore’s commitment to sustainability and a greener future. The adoption of AMDs also reflects a shift towards more inclusive urban planning, where mobility solutions cater to a broad spectrum of users, including the elderly and those with disabilities, thus promoting a more cohesive and accessible urban community.
The integration of AMDs into Singapore’s urban mobility ecosystem marks a significant stride towards a sustainable, efficient, and inclusive transportation network. As these devices continue to evolve and adapt to the needs of Singapore’s dynamic urban landscape, their role in shaping a more connected and environmentally conscious city becomes increasingly pivotal.
Safety Regulations and Their Impact on AMD Usage in Singapore
Establishing a Robust Regulatory Framework
Singapore has been at the forefront of implementing comprehensive safety regulations for AMDs, ensuring that the convenience and efficiency these devices offer do not compromise public safety. The introduction of the UL2272 certification standard for PMDs marks a critical step in this direction. This certification demands rigorous testing of electrical and fire safety standards, mitigating the risk of fire incidents that have been associated with these devices in the past. Similarly, PABs and PMAs are subject to stringent safety requirements, including specifications for construction, performance, and usage to ensure they are safe for both the users and the public.
The Impact of Regulations on Safety and Compliance
The implementation of these safety standards has had a tangible and positive impact on reducing fire incidents and enhancing the overall safety of AMD users in Singapore.
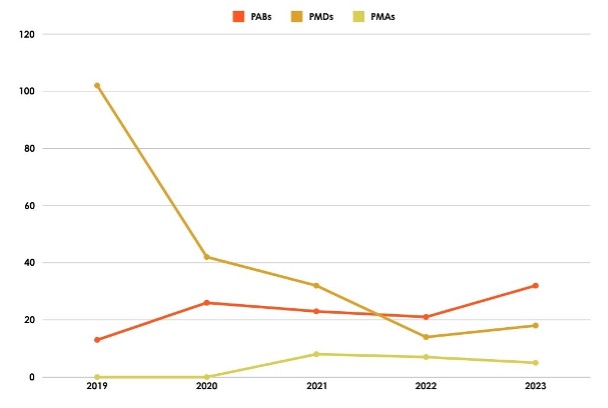
Fire Incidents involving AMDs in the last 5 years (2019-2023)
Source Data: Singapore Civil Defence Force
The graph depicts a clear downward trend in the number of fire incidents involving AMDs from 2019, underscoring the effectiveness of the regulatory measures. It not only highlights the significant decrease in such incidents but also emphasizes the role of stringent safety standards in protecting the community.
A Commitment to Ongoing Safety
The successful reduction in fire incidents and the enhanced safety of AMD users are testaments to Singapore’s proactive approach to regulation and enforcement. By continuously refining and updating these regulations, Singapore remains committed to ensuring that AMDs contribute positively to urban mobility without compromising the safety of its citizens. This ongoing effort fosters a culture of responsibility among manufacturers, retailers, and users, ensuring that the benefits of AMDs are enjoyed within a framework of safety and respect for public welfare.
Remaining Risks and Challenges in AMD Safety
Persistent Fire Risks amid Regulations
Despite the successful implementation of regulations like the UL2272 certification, fire risks associated with AMDs have not been entirely eliminated. Several factors contribute to the persistence of these risks:
- Non-Compliance: Not all users and retailers strictly adhere to the regulations. The use of non-approved devices that have not undergone rigorous safety testing continues to be a concern.
- Improper Charging Practices: Many fire incidents are attributed to improper charging practices, including overcharging, using incompatible chargers, or charging in unsafe conditions, which can lead to overheating and potential fires.
- Wear and Tear: Regular use of AMDs inevitably leads to wear and tear, which can compromise the integrity of electrical components and batteries, increasing the risk of malfunctions and fires.
Challenges in Ensuring Comprehensive Compliance
The AMD ecosystem in Singapore is diverse, encompassing users, retailers, and manufacturers. Ensuring that all stakeholders adhere to safety norms presents several challenges:
- Sourcing of Non-Approved Parts: The availability of non-approved AMD parts, often sourced from other countries such as China, poses a significant challenge. These parts, while often cheaper, may not meet the safety standards required in Singapore, leading to increased risk when they are used in repairs or modifications.
- Education and Awareness: Despite ongoing efforts, there remains a gap in education and awareness about safe charging practices and the risks of using non-compliant devices and parts. Bridging this gap is essential for reducing fire incidents.
- Enforcement: Effective enforcement of regulations across the entire AMD ecosystem is challenging. It requires not only stringent checks but also cooperation from all parties involved, from end-users to importers and retailers.
Preventive Measures and Best Practices for AMD Safety
Navigating the complexities of AMD safety requires adherence to best practices and preventive measures. These guidelines ensure the safe usage, maintenance, and storage of AMDs, significantly reducing the risk of fire incidents and enhancing overall safety for users and the community.
Selecting Safe and Compliant AMDs
- Choose Wisely: Opt for AMDs that are certified with safety standards, such as the UL2272 certification for PMDs. Ensure that PABs and PMAs also meet the requisite safety criteria set forth by Singaporean authorities.
- Purchase from Reputable Sources: Buy AMDs and their components from reputable retailers who comply with national safety regulations. This reduces the risk of acquiring substandard or non-compliant devices.
Charging Practices to Prevent Fires
- Follow Manufacturer’s Instructions: Always charge your AMD according to the manufacturer’s guidelines. Use the original charger provided, and avoid overcharging by unplugging the device once it is fully charged.
- Safe Charging Locations: Charge your AMD in a well-ventilated area, away from flammable materials. Do not charge devices unattended, especially overnight.
Maintaining and Storing AMDs Safely
- Regular Checks and Maintenance: Perform regular inspections of your AMD for any signs of damage, especially to the battery and electrical components. Address any issues immediately with professional repair services.
- Proper Storage: Store your AMD in a cool, dry place to prevent exposure to adverse conditions that can degrade batteries and electrical components, increasing the risk of malfunction.
By embracing these preventive measures and best practices, users can contribute to a safer environment for everyone, ensuring that AMDs remain a beneficial and secure mode of urban mobility. Compliance with these guidelines not only safeguards the individual user but also the broader community from potential fire hazards associated with AMDs.
Handling AMD Fire Incidents: The Role of Insurance and Expert Restoration
Despite rigorous safety measures and preventive practices, fire incidents involving AMDs can still occur, presenting a challenge for homeowners. When faced with the aftermath of an AMD-related fire, the path to recovery involves several crucial steps, including the potential involvement of insurance. However, it’s important to note that insurance coverage may not extend to all incidents, especially if negligence or unauthorized modifications of the AMD contributed to the fire.
In the unfortunate event of a fire caused by an AMD, homeowners should first ensure the safety of all occupants and then contact their insurance provider. Providing a detailed account and evidence of the incident is crucial. However, insurance policies vary, and cases involving negligence or the use of non-compliant parts might not be covered. This underscores the importance of adhering to safety standards and using approved devices and components.
Big Red Pte Ltd: A Beacon of Restoration
In instances where fire damage occurs, a recovery specialist such as Big Red Pte Ltd, a leader in disaster restoration services in Singapore, steps in to provide expert fire and soot damage restoration. With a deep-rooted commitment to creating safe, clean, and healthy environments, Big Red restores affected homes to their pre-incident state.
Case Study: Fire Restoration in a Bedok HDB Corridor
Incident Description: A fire, initiated by a malfunctioning PMD erupted in the common corridor of a residential block in Bedok. The incident occurred late in the evening, quickly filling the corridor and adjacent residential units with dense smoke and leaving behind substantial soot and smoke damage.
Project Scope: The project involved the complete restoration of the fire-affected corridor and the interiors of adjacent units that suffered collateral damage from soot and smoke infiltration. The goal was to return these areas to their pre-incident state, ensuring they were clean, safe, and habitable once more.
Damaged Areas: The fire predominantly damaged the corridor, affecting walls, ceilings, and flooring with soot and smoke residue. Additionally, several adjacent units experienced smoke damage, particularly in terms of discoloured walls and embedded smoke odors in fabrics and furnishings.
Restoration Approach: Big Red’s approach was methodical and comprehensive, involving several key steps:
- Soot and Debris Removal: Initial cleaning to remove all soot and debris from the corridor and affected units.
- Smoke Odor Elimination: Employing advanced deodorization techniques to eliminate smoke odors, ensuring no residual smells were left.
- Deep Cleaning and Sanitization: Thorough cleaning of all surfaces, along with sanitization to ensure a healthy living environment.
- Restoration and Repainting: Repairing damaged infrastructure, followed by repainting to restore the aesthetic appeal of the corridor and units.
Final Outcome: The restoration project was completed successfully, with the corridor and impacted units restored to their original condition. Residents were able to return to a safe, clean, and odor-free environment, where the project not only underscored Big Red’s expertise in disaster restoration but also reinforced the importance of safety and preparedness in the face of potential fire risks associated with AMDs.




As the landscape of urban mobility evolves with the increasing use of AMDs, the commitment to safety and preparedness becomes more critical than ever. While advancements and regulations have significantly reduced the number of fire incidents, the responsibility lies with each user to maintain vigilance and adhere to established safety practices. In times of need, remember that Big Red Pte Ltd is here to support you with professional restoration services, ensuring your environment is safe, clean, and quickly restored to its pre-incident condition.
If you ever find yourself facing the aftermath of an AMD fire, don’t hesitate to reach out. Contact us at info@bigred.com.sg or call our emergency hotline at 92229222. Our team of experts is ready to assist you 24/7, providing the swift and effective response needed to address your concerns and restore your peace of mind.




